Mobile money services
Popular with employees and customers alike
Electronic money transfers in Africa are done via mobile phones that have been registered by a mobile-phone company. Thus, major players in the electronic transactions business are subsidiaries of mobile-phone companies.
The telecommunications company MTN Zambia operates MTN Money, while Airtel manages a brand known as Airtel Money. The third major player is Zoona, a mobile transaction company that is not a mobile-phone subsidiary, but uses all phone networks. It has support offices in South Africa and mobile transactions payment systems in Zambia, Mozambique and Malawi.
Since the beginning of its operations in 2007, Zoona has transmitted over $ 2 billion in mobile transactions. The company has grown exponentially and now has an estimated 1,500 outlets, mostly small booths, throughout Zambia.
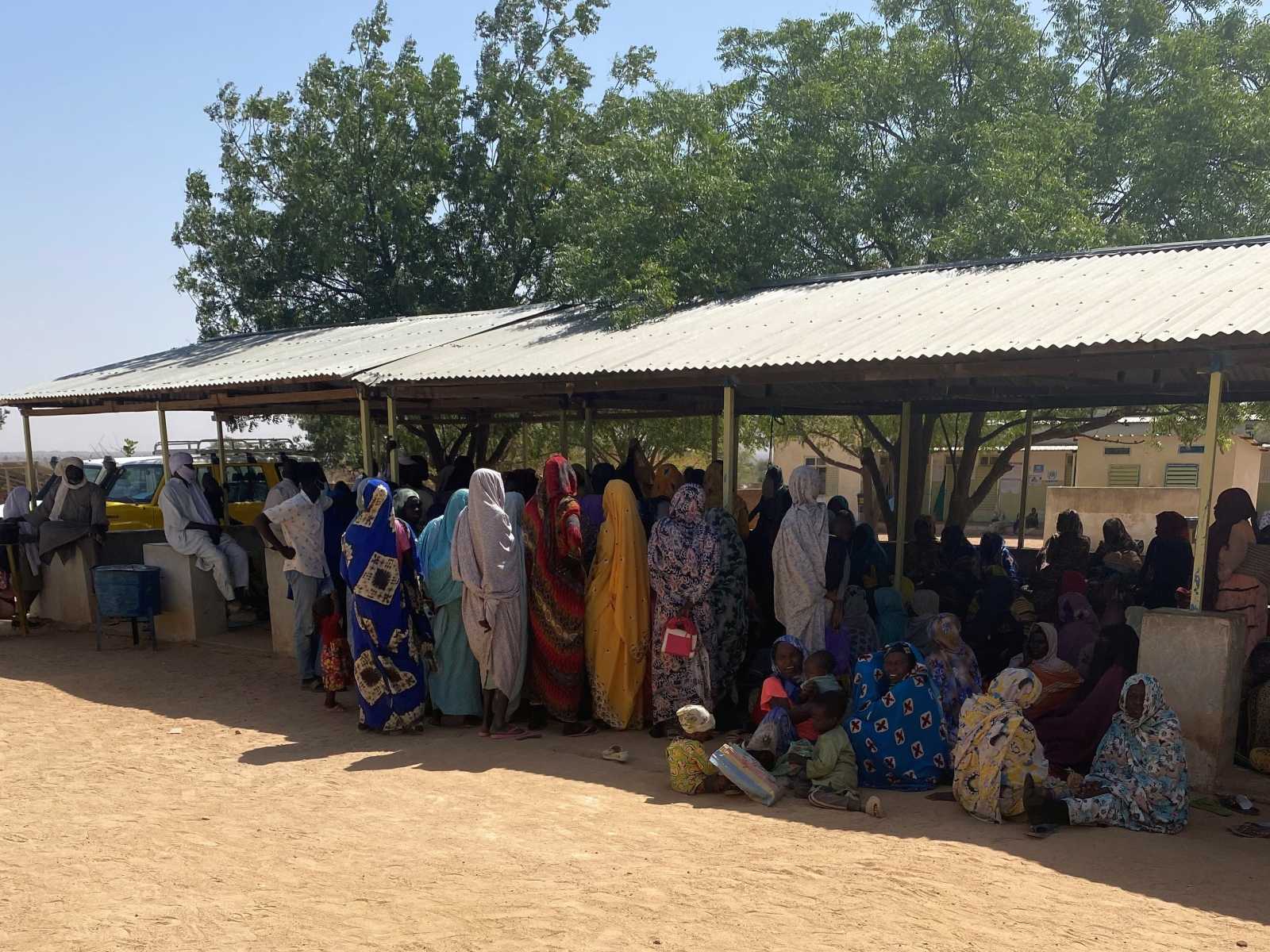
These booths are operated by agents, many of them girls and young women without tertiary education. Typically, they don’t have the start-up capital required for operating a mobile money booth in Zambia. However, Zoona provides them with funds to open a booth, thus giving them the chance to become financially independent.
Some of them have higher ambitions too. Naomi Magau, who works as a mobile money agent in Ndola, gets a regular salary every month. “The owner of the booth from which I operate is now at college,” Magau says. The young woman is planning to do the same and “use the salary I get to pay for my college education”.
Money booths are very popular, because mobile money companies provide saving features on mobile-phone systems that serve rural people or the urban poor who have no bank accounts. For instance, MTN Zambia has partnered with Barclays Bank to provide customers with small loans that they access electronically using mobile phones.
Ben Kabwe, a resident of the city of Ndola, says he is able to save money because “mobile money companies don’t charge account fees like banks do”. He goes to the money booth whenever he wants to withdraw cash.
According to the Bankers Association of Zambia, taking all mobile transaction companies together, there were 304 million mobile transactions in 2018, combined worth $ 2.2 billion. The prerequisites to use the system are good: according to Zambia’s Information Communications Technology Authority (ZICTA), mobile-phone penetration in the country is at 91.61 % – well ahead of mobile internet, fixed land phone and fixed internet penetrations, which are all below 60 %.
Link
Zambia Information and Communications Technology Authority (ZICTA) statistics portal:
http://onlinesystems.zicta.zm:8585/statsfinal/
Humphrey Nkonde is the assistant to the editor-in-chief at Mission Press and a media researcher based in Ndola, Zambia.
humphrey_nkonde@ymail.com